There are several sources of customer data you can use to understand your customers better and drive business growth.
Website analytics helps you improve overall user experience and evaluate the effectiveness of marketing campaigns. Transactional data helps you understand buying patterns and identify customer segments and cross-selling opportunities. You can also get more data from social media and even customer support.
But all this scattered data makes it difficult to draw any meaningful conclusions. It’s like opening up a book and starting from the middle or trying to imagine what a jigsaw puzzle looks like when all you have is a few random pieces.
Without context, all this data is meaningless. You can use the micro pieces of data for campaign optimization, but at the end of the day, you need to understand how all this data fits into the big picture.
In this article, you’ll learn:
- The types of customer data
- The techniques for capturing customer data
- Key metrics for analyzing data
- How to use this data for business growth
- How EngageBay can be your one true source of customer data
Table of Contents
What Is Customer Data?
Customer data is any information you collect and store about your customers. Customers can give out these details from surveys, online forms, account registration, transactions, loyalty programs, and social media interactions.
Or, you can gather them in the form of interactions they had with your business.
You can then analyze this data to identify potential buying patterns, map the customer journey to improve customer experience, and personalize marketing campaigns based on customer behavior.
But how you look at customer data matters. You can either group data in a way that makes it easy for you to focus on what drives growth or makes it difficult to transform data into meaningful insights.
What Are The Types of Customer Data?
Christina Inge, author of “Marketing Metrics: Leverage Analytics and Data to Optimize Marketing Strategies,” introduces four types of customer data.
She calls them the core four:
- Revenue-based metrics
- Conversion metrics
- Communications data
- Customer loyalty, value, and retention data
“You look at them to understand how you’re interfacing with your customers and how you can best serve them, “ she says. “How you can convert more customers and how you can retain more customers which is what business is all about.”
As she reiterates in her book, these are not the only ways of looking at your customer data. The conventional way of grouping data is into first-party data, second-party, third-party, and zero-party data.
But I found Christina’s ways to be more practical, and as she says in her book,
“… They are a framework that helps you focus your analysis based on results.”
Revenue-based metrics
These are data that help you identify which customer segment drives the most revenue. This data helps you narrow down to your most valuable customers who contribute more to your revenue than others. These are the customers you would offer exclusive offers, upsell and cross-sell.
But the main reason this data is crucial is because it shows patterns of your most valuable customers.
For example, you might find most of them with a higher customer lifetime value (CLV) are acquired through ABM strategies and less through SEO content. So you’ll invest more in the channels of acquisition that bring in high CLV customers because those are the ones with higher ROI.
But where do you begin your customer revenue metrics analysis?
Christina recommends you begin on the individual customer level. This will help you in two ways:
- Identify how to improve the customer experience of your best customers
- Identify patterns that you’ll use for segmentation
Here’s the data that Christina recommends you can look for when analyzing your individual customer revenue metrics:
- Most recent purchase date
- Purchase frequency: How often does the customer make a purchase? How does it compare to the overall average and to customers in the same segment?
- Number of purchases by month, quarter, and year.
- Customer lifetime value (CLV): Is this value increasing or decreasing?
- Average order size, this metric represents the average value of a customer’s purchases.
- What product did they recently buy? Is this product typical of their usual buying behavior?
- Most frequent purchase
The patterns you notice when analyzing this data should be from a number of customers. This will provide concrete evidence of insights you can use to create personalized marketing campaigns.
Conversion metrics
The revenue-based metrics gave you a glimpse of who your best customers are. Conversion metrics help you track back the steps they took from awareness to conversion.
This data tells you how a customer found you and what made them convert. You can analyze conversion metrics using the following data recommended in the book:
- Acquisition channel: which channel did the customer come from, and what channels did you engage with them before they converted?
- Acquisition message: What was the message that led to the conversion?
- How many touches did they need to convert?
- What conversion path did they take to arrive at converting? They may have started with an SEO article, come back through a LinkedIn link, signed up to an email pop-up a few weeks later, and a month later converted with your email offer.
This will help you understand what channels, what messaging, and which calls-to-action (CTAs) drive the majority of the conversions.
Let’s say you run an e-commerce store that sells athletic shoes. Through analyzing your conversion metrics, you discover the following customer journey:
Acquisition Channel: The customer initially discovers your brand through an Instagram ad showcasing a new line of running shoes.
Acquisition Message: The ad emphasizes the shoes’ lightweight design and advanced cushioning technology, highlighting their superior performance and comfort.
Touches Needed to Convert: The customer engages with your brand multiple times before making a purchase. After seeing the Instagram ad, they visit your website to browse the available shoe models. A week later, they come across a positive review of one of your shoes in a fitness blog, which reinforces their interest. They then sign up for your newsletter to receive updates on new product releases. Finally, two weeks later, they receive an email showcasing a limited-time discount on the specific shoe model they were considering, which prompts them to make the purchase.
Conversion Path: The customer’s journey involves multiple touchpoints across different channels. They initially find your brand through an Instagram ad (Acquisition Channel). They then continue their research by visiting your website and reading a positive review on a fitness blog (additional touchpoints). After signing up for your newsletter (another touchpoint), they receive a targeted email offer that convinces them to convert (final touchpoint).
By understanding these conversion metrics and the customer journey example, you can optimize your marketing efforts by focusing on the most effective acquisition channels, refining your messaging to align with customer preferences, and optimizing touchpoints to streamline the conversion process.
Read also: How To Optimize Your CTR With eCommerce Email Heatmap Analysis
Communications data
While conversions data help you trace the customer journey and optimize your marketing campaigns, communications data helps you retain customers.
This data tells you what resonates with your customers, which you’ll use to optimize your marketing efforts.
By analyzing communication data such as customer inquiries, feedback, and interactions, you can gain insights into what customers value, what their pain points are, and how to address them.
Here are the data points to look for when measuring your communication with customers:
- Email open rate: Frequency and recent changes? What events caused sudden increases or decreases? For example, a customer service call may have affected open rates negatively, while a satisfying purchase could have strengthened brand affinity.
- Click-to-Open rate: This is the percentage of people who opened your email and clicked on a link. Signs of customer churn include decreased email engagement, while increased engagement may indicate readiness for a purchase.
- Top email topics: What topics have the highest click rate? You might be sending newsletters to customers about various topics such as skin care tips, natural ingredients, self-care routines, and healthy lifestyle habits. By analyzing the click rates of different email topics in your past communications, segmented by customer, you may discover that emails about natural ingredients generate higher engagement compared to self-care routines. This data helps build a customer persona profile, focusing on individuals who prioritize organic and natural skincare options.
- Social media engagement: Do they follow you on any platform or engage with your content?
- Reviews: Look for both negative and positive reviews. Negative reviews may show which segment of customers aren’t your target audience, while positive reviews show you what customers love about your product, and they can be considered for special offers.
Use this data to understand what resonates with your customers and improve your marketing efforts accordingly, ultimately reducing churn.
Read also: How To Perfect Your Customer Data Governance
Customer loyalty, value, and retention data
This data can help you identify customers who are most likely to stay loyal to your brand. Christina recommends asking yourself the following questions when measuring customer loyalty:
- What is the average customer retention period? Does it vary across segments? If so, what is the average tenure for each segment?
- How frequently do customers make purchases?
- What signs indicate that a customer is likely to churn? Do they abandon carts frequently, purchase specific products, or contact customer service with specific complaints?
- What signs indicate that a customer is likely to increase their loyalty, such as switching to an annual subscription or upgrading services? What actions do they take beforehand?
Read also: Customer Profile: How to Create One Using CRM Software
CRM Data: The Core of Your Customer Data
A CRM helps you manage your customer relationships. It does this by capturing, storing, and analyzing customer data from a variety of sources, such as website analytics, transactional data, social media insights, and customer support.
With a CRM like EngageBay, you can easily organize and interpret customer data. You can track revenue-based metrics, such as identifying which customer segments drive the most revenue.
This helps you focus on your most valuable customers and offer them exclusive deals or suggest relevant products to cross-sell or upsell.
Read also: 13 Customer Profile Software Tools for Better Sales Pitches
EngageBay CRM also helps you understand the steps customers took from initial awareness to making a purchase. You can analyze acquisition channels, messages that led to conversions, and the conversion path itself.
This information helps you pinpoint which channels, messages, and touchpoints are driving the most conversions, so you can optimize your marketing efforts accordingly.
A CRM also lets you analyze customer inquiries, feedback, and interactions. This gives you valuable insights into what resonates with your customers. You can keep track of email open rates, click-to-open rates, and even social media engagement.
This data guides you in optimizing your marketing campaigns to serve your customers’ interests better and reduce churn.
To analyze data, you first need to capture customer data.
Read also: 10 Leading Customer Tracking Software For 2024 [Micro Reviews]
How Is Customer Data Collected?
Some common methods of collecting customer data include the following.
Lead capture forms
You can gather valuable information from interested leads and potential customers by strategically designing and optimizing lead capture forms.
EngageBay is a CRM and marketing automation software, so it lets you create forms and landing pages. There are two types of forms that you can use to capture customer data from website visitors:
- Inline forms
- Popup forms
You can customize the forms to appear as pop-ups, stick to the top of the page, or pop up on either side. You can also edit your call to action, set a featured image for the form, choose a design, and send double opt-in emails to confirm new contacts.
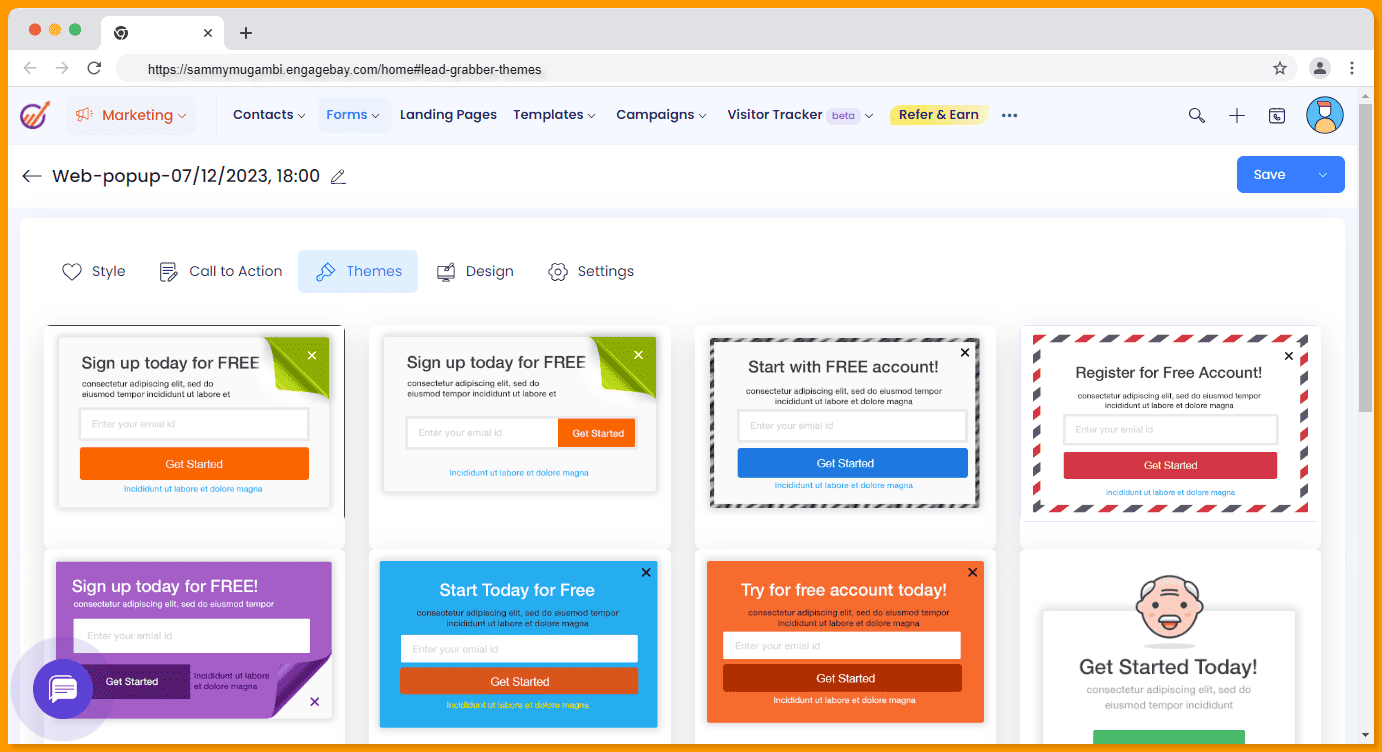
To create effective lead capture forms, you should focus on the following:
- Form design and user experience: Forms should be simple, concise, and easy to complete. They should also have clear and compelling calls-to-action.
- Incentives or benefits: You can offer incentives or benefits in exchange for completing the form, such as exclusive discounts or valuable content.
- Placement and visibility: Forms should be placed on relevant web pages, such as landing pages or product pages.
- A/B testing: You should A/B test different form variations to identify the most effective design for data collection.
- Privacy policy: You should clearly communicate to users that their data will be handled securely and in compliance with privacy regulations.
- CRM integration: You can connect forms to CRM systems to automate data entry, improve lead management, and streamline follow-up processes. (EngageBay makes it simple to create forms and manage customer data directly on the platform).
- Data analysis: You can analyze the submitted information to identify potential customer segments, understand buying patterns, and uncover cross-selling opportunities.
By following these tips, you can create effective lead capture forms that will help you gather valuable customer data and drive growth.
Read also: Best Free Lead Management Software for Small Businesses
Customer surveys
Customer surveys are a powerful tool for gathering valuable insights into customer preferences, satisfaction levels, and buying behaviors. To use them effectively, follow these tips:
- Design effective surveys: Define clear goals and objectives, use clear and concise language, and employ a mix of question types to collect comprehensive data.
- Maximize response rates: Clearly communicate the survey’s purpose, use appropriate channels to reach your target audience, offer incentives for participation, and address barriers such as mobile accessibility and minimal required fields.
You can use tools like Typeform, SurveyMonkey, and JotForm to create these surveys.
Read also: A Guide To Enhancing Customer Data Management
Website analytics
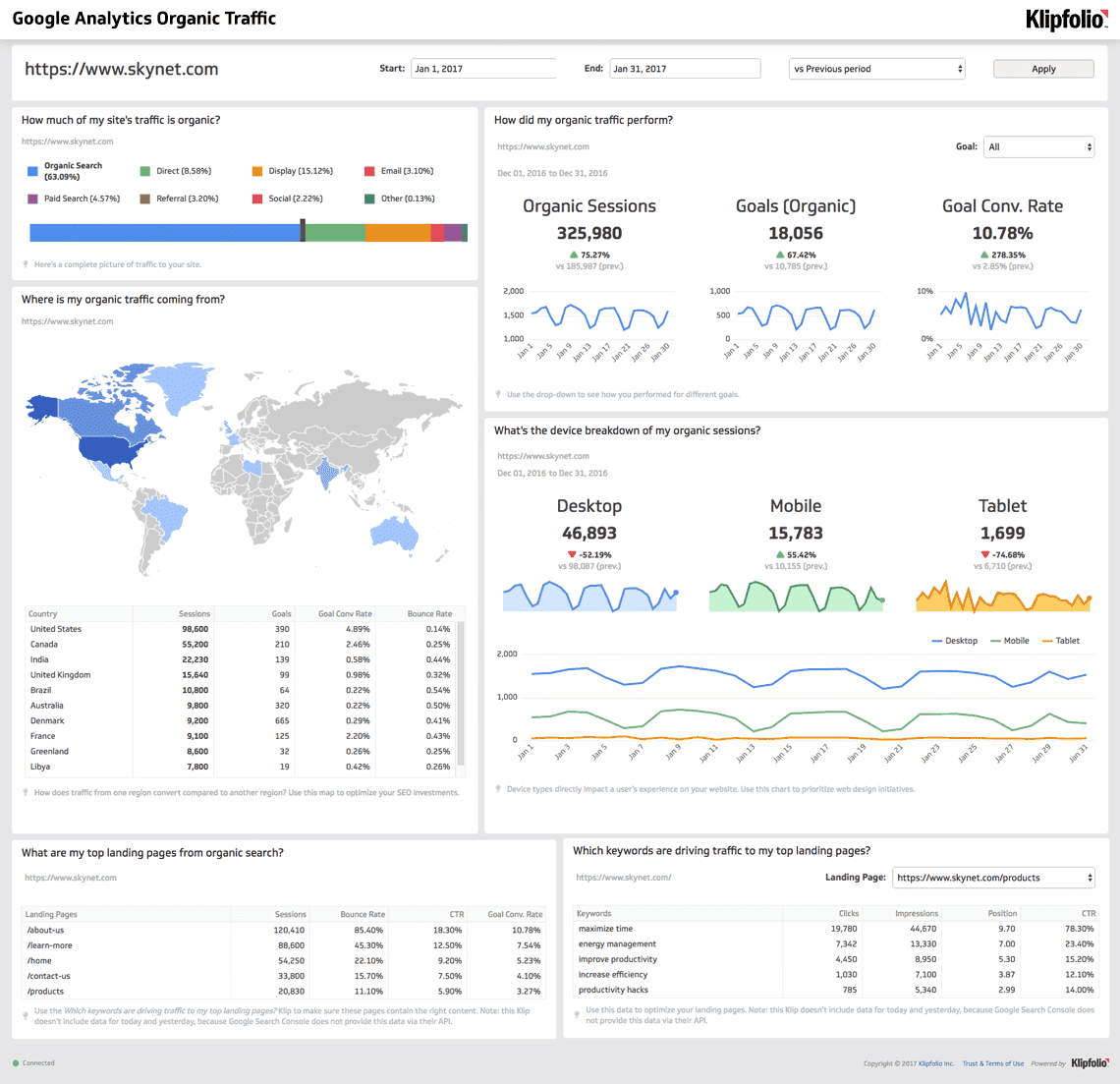
Website analytics provides you with a wealth of data on user behavior and the effectiveness of your marketing efforts. You can find this data on your Google Analytics page.
Website analytics can help you track website visitors, analyze their demographics, and understand their browsing patterns. Additionally, it can help you evaluate the performance of marketing campaigns and channels, providing valuable insights into customer acquisition and engagement.
Some of the key metrics that website analytics can provide include visitor traffic and sources, bounce rate, conversion rate, time on page, page views, and exit pages. By analyzing these metrics, you can gain a deeper understanding of user preferences, improve user experience, and identify areas for improvement.
Here are some specific examples of website analytics. You can use:
- Visitor traffic and source(s) data to identify which marketing channels are most effective at driving traffic to your website.
- Bounce rate data to identify which pages on your website are not engaging visitors.
- Conversion rate data to identify which pages on your website are most effective at converting visitors into customers.
- Time-on-page data to identify which pages on your website are most interesting to visitors.
- Page views data to identify which pages on your website are most popular with visitors.
- Exit page(s) data to identify which pages on your website are causing visitors to leave.
Read also: A Definitive Guide To Customer Data Analytics
Web tracking
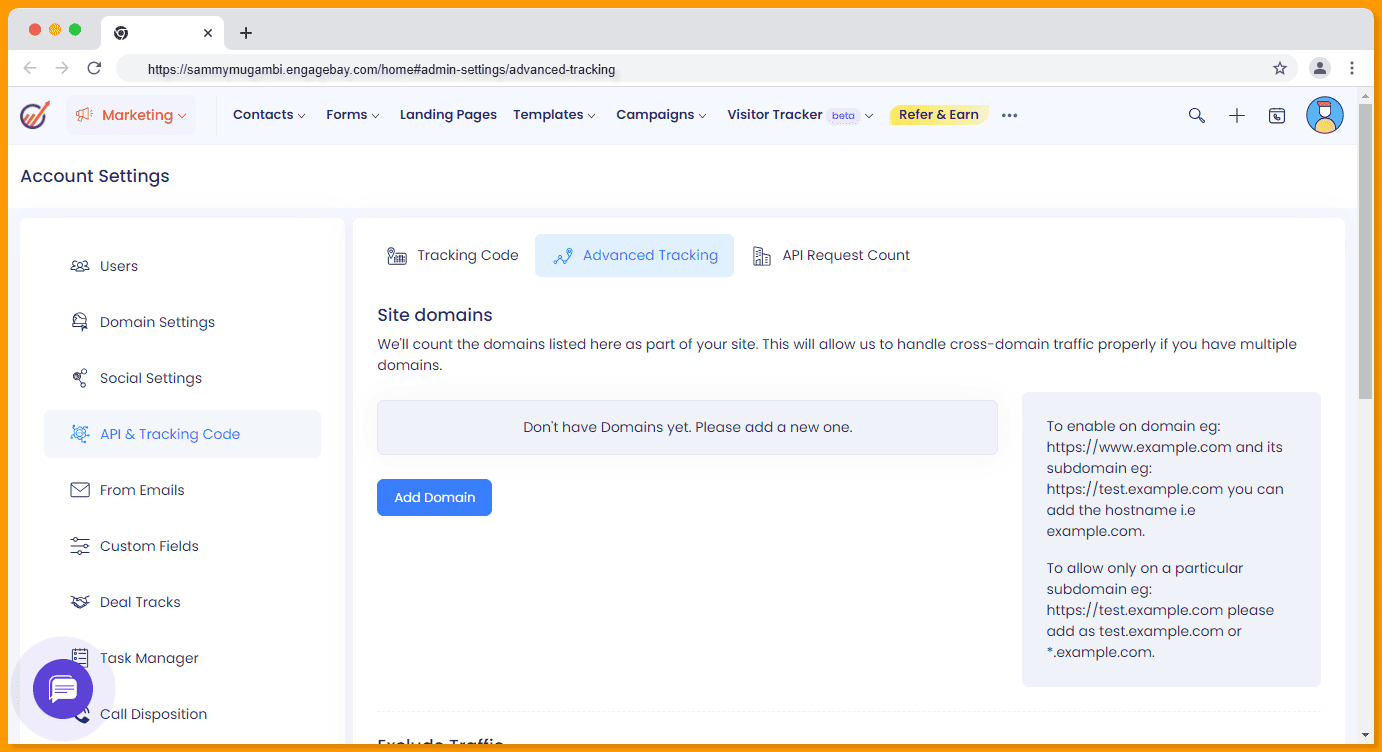
You can effectively track and analyze customer interactions on your website by using website tracking tools like EngageBay.
One essential functionality is the ability to identify visitors by their email addresses. When a visitor’s email matches an existing contact in EngageBay, the contact record is updated, and all the collected page view data is associated with that contact.
This gives you a comprehensive record of each contact’s website activity, providing valuable insights into their engagement.
Tracking page views is another crucial aspect of website tracking. EngageBay automatically tracks pageviews when the tracking code is loaded on a webpage.
In a single-page application, you can manually call the tracking function to track subsequent views. This ensures that you have a complete understanding of the specific pages visited by customers, allowing you to analyze customer interests and preferences.
Read also: Mastering Customer Data Integration: Process and Strategies
Tracking interactions with customer support
You can collect valuable data about customer concerns, issues, and preferences by tracking customer support interactions. This data can be used to understand customer needs, evaluate satisfaction levels, and identify areas for improvement.
EngageBay’s helpdesk software enables you to do this by providing a variety of features, such as ticketing systems, an inbuilt CRM, live chat transcripts, and recorded customer support calls.
Here are some specific examples of how you can use the data collected from customer support interactions:
- Identify common customer issues: You can identify common problems and develop solutions by tracking the types of issues that customers are experiencing.
- Improve support workflow: Tracking the steps involved in resolving customer issues will allow you to identify areas where the process can be streamlined. This can lead to faster and more efficient support.
- Deliver exceptional customer experiences: You can provide exceptional customer experiences by using the data collected from customer interactions. This can lead to increased loyalty and advocacy.
Read also: Top 9 Customer Data Platforms With Pros And Cons
Conclusion
Mastering customer data is the key to unlocking growth and delivering exceptional customer experiences. With EngageBay CRM, you can effectively capture and interpret customer data, leading to personalized strategies that drive results.
By tracking customer data and analyzing the customer journey, you can identify your most valuable customers, optimize marketing efforts, and offer tailored experiences.
EngageBay also enables the analysis of customer inquiries and interactions, providing valuable insights for campaign optimization and reducing churn.