Email remains a top marketing channel, with 79% of marketers ranking it among their top three tools. This is why understanding domain reputation and the strategic use of email subdomains is crucial.
Email subdomains, the part after the ‘@’ symbol (e.g., [email protected]), have become vital in business communication. They enhance brand presence, add authenticity, and streamline customer interactions by clearly designating different departments or purposes.
Businesses can use subdomains to send transactional, marketing, and cold emails, boosting engagement and improving customer experiences.
In this blog post, let’s explore how email subdomains can improve deliverability and strengthen your connection with consumers.
Let’s get started!
Table of Contents
What Is an Email Subdomain?

Before understanding what a subdomain is, let’s first familiarize ourselves with what a domain is.
A domain is a distinct, easily understood method of identifying a website, often called the root or parent domain. For example, you are now on the engagebay.com domain. The Domain Name System (DNS) links the domain name to a specific IP address.
Conversely, a subdomain is a prefix that appears before the parent domain and after the ‘@’ symbol in email addresses. Websites often use subdomains to route traffic to another IP address while maintaining access to the main domain.
For instance, in the email address [email protected], ‘query.’ is the subdomain part of the main domain, ‘business.com.’

The question remains: what distinguishes an email subdomain from an email domain?
The most popular method for sending and receiving business emails is through email domains. Using a @yourdomain.com address makes your company appear far more professional than using a @gmail.com or @yahoo.com address.
Many firms use their root domain, or primary domain, for business correspondence, making it simple to verify that the email is from the organization.
However, this approach can impact email deliverability and reputation if not managed properly, especially if different types of emails, such as transactional and promotional, are sent from the same domain without precise segmentation.
For instance, if all business emails from a company are sent from abcxyz.com, it can lead to deliverability issues.
An email subdomain, separated by a dot/period, is added before the main domain and is used to send emails instead of the root domain. This allows for better segmentation and management of different types of emails.
Benefits of Using Email Subdomains
If you think tracking and organizing are the only benefits of email subdomains, you’re missing out on significant opportunities.
Internet Service Providers (ISPs) treat email subdomains as separate entities from the root domain. This move significantly enhances your email deliverability by reducing the chances of your emails ending up in spam folders.
Many companies are shifting to using multiple subdomains to manage their email communication better. This strategy helps you organize your email list more effectively, streamline communication channels and strategies, and avoid spam folder issues due to multiple emails from the same subdomain.
Here’s a deeper look.
Improve deliverability
How do subdomains improve your email deliverability?
It’s simple. They make different emails from the same company look like they’re coming from other entities through different subdomains. So, if your emails end up in the recipient’s spam folder, you might not be doing it right.
Get multiple subdomains and segment them based on different aspects of your company, such as promotions and PR, order updates, customer support, and so on.
This way, you enhance not only your subdomain reputation but also the effectiveness of your email communication.
Organize your subdomains
As mentioned, creating subdomains for different communication aspects is a surefire way to better organize and streamline your communication. This will help you keep your company’s services distinct and organized.
Track and analyze
Since your communication is well segregated and organized, you can get data from different segments more accurately. This can enhance your efficiency in reading data, tracking performance, and performing better analytics.
This way, you learn what went wrong and where in less time than it takes to deal with cumulative data.
You can also enhance your content by seeing which type of email content performed better and with which audience.
Control sender reputation
Maintaining a positive sender reputation is essential for email deliverability, and it’s all for good reasons. Whether or not you’re using subdomains for your company will impact your sender’s reputation.
This happens because these shield your parent domain by bearing the brunt of being blocklisted in case of a damaged reputation.
Improve security
In today’s cybersecurity environment, it is crucial to boost email security. Using a unique domain name for emails allows specific security measures to enhance email data defense safely.
Other email authentication techniques, such as DKIM, DMARC, and SPF, become more accessible when using a subdomain.
These protocols confirm that your messages are genuine. And that they have not originated from some fake domain. It is common in spam and phishing scams, making the sender’s security and recipients more secure.
Separate email marketing from central communication
Organizing email marketing activities through subdomains helps avoid negative associations.
For instance, if a subdomain is underperforming and harms its reputation, your central communication channel, which is your parent domain and other healthy subdomains, remains protected.
Through this segregation, there is a guarantee that the primary domain for each brand does not compromise the other’s perception. This builds trust and credibility among the audience.
Read also: What Is Domain Reputation and How Can You Improve It?
How to Set Up an Email Subdomain
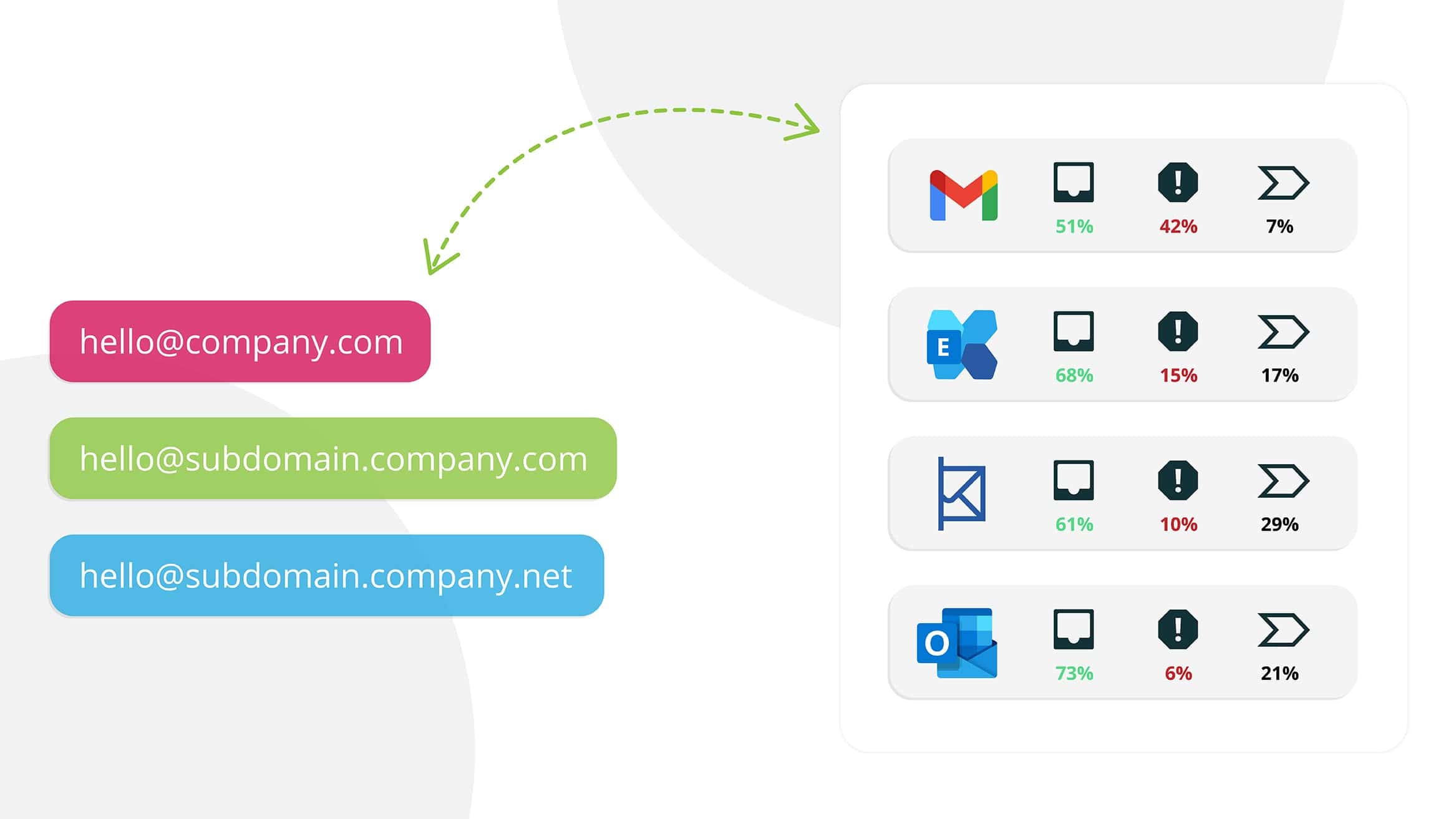
Now that you know how subdomains can benefit your business’s bottom line, it’s easier to understand how to set it up. In this section, we will examine the essentials of setting up an email subdomain.
Choose a subdomain
First and foremost, pick a name that resonates with the use case and reflects your brand identity well.
Your subdomain can be creative while staying in line with the purpose it’s going to serve, such as promotion or transactional emails. Such as “email.yourdomain.com” or “news.yourdomain.com“.
After that, you need to set up authentication protocols from the beginning to ensure your emails find their proper and intended path.
Access DNS settings
Log in to your domain registrar or DNS provider’s dashboard.
Create a CNAME record
Come up with a CNAME that aligns with the context of your preferred subdomain. CNAME records allow you to alias one name to another. The term CNAME refers to the Canonical Name. It points a name to another name instead of to an IP.
For example, using Google Workspace, the CNAME might point to “ghs.googlehosted.com.”
Update MX records
This step is to edit or add the MX (Mail Exchange) records to point to the server responsible for your mail. Your email service provider generally supplies this and helps ensure your emails to your subdomain reach the correct destinations.
Best practices for integrating with email service providers
- Verify Ownership: Before you set up your subdomain, some email services will ask you to verify your parent domain. They generally provide instructions there, so follow along.
- Configure SPF and DKIM: Set up SPF (Sender Policy Framework) and DKIM (DomainKeys Identified Mail) records, which are crucial for securing your email and improving deliverability.
- Test Configuration: Now that you’ve set up the whole thing, don’t forget to test-run it. Check its configuration to ensure everything appears as intended. You can also find some tools that these email providers will suggest. That way, you can validate your setup.
Additional tips
- Backup Existing DNS Records: Backing up your existing DNS records can help you with unintended troubleshooting. So before you make any changes and your previous configurations are lost for good, make sure to back up your existing DNS records.
- Monitor Propagation: A plethora of DNS lookup tools can help you track the changes you’ve made to appear globally. This propagation usually takes forty-eight hours.
- Seek Professional Help if Needed: When you can’t crack the case, seek out those who know it better. Seek help from IT experts, or reach out to your DNS provider. A little help can save you a lot of time.
Read also: Reverse DNS Lookup — Complete Guide for Small Businesses
Best Practices for Managing Email Subdomains
Managing email subdomains can be a no-brainer, especially if you do it to maintain optimal performance and organization. Let’s check out some best practices for you to manage your email subdomains better:
Segmenting different types of emails
- Identify email categories: See how many email types your firm has, such as marketing, notifications, support, transactional, order updates, etc.
- Use subdomains for segmentation: Assign these types a suitable name for their purpose. For example, your subdomain name can be ‘promotion.yourdomain.com’ for promotional emails.
- Implement clear naming conventions: A name that immediately states the purpose of the emails is the only one suitable for a subdomain name.
Regular monitoring and maintenance
- Monitor deliverability: Regularly check the deliverability performance to avoid potential issues that can become bigger later.
- Audit email lists: Regularly review and clean up your email lists to remove inactive or unengaged subscribers, improving overall email performance. Keep sweeping and cleaning your email list. Skim through and find the ones that do not interact or seem to have been dormant addresses. Edit them out. You need results from active users.
- Update SPF and DKIM records: Monitor and update SPF and DKIM records periodically to keep your email authentication and security robust.
Common mistakes to avoid
- Overcomplicating subdomains: Be mindful of crowding your email subdomain list. Keep your repository of email subdomains clean and sorted. That way, you can access, organize, and manage them better.
- Neglecting DNS maintenance: Another common mistake is ignoring DNS maintenance. Your deliverability will likely suffer if you ignore crucial DNS monitoring and updates.
- Skipping testing: Testing new setups regularly and ensuring everything is as intended can save a lot of time in the future.
Documentation and onboarding
- Maintain documentation: Keep the records and documents of your subdomain in hand and safe. This is a crucial precautionary habit that helps troubleshoot and maintain a healthy email setup.
- Training and onboarding: Ensure that everyone involved in managing email subdomains knows what they’re doing. Their training shouldn’t be ignored.
Review and adapt
- Regular reviews: Take frequent reviews from your testers and see if there are areas for improvement.
- Stay informed: Keep informed on the email subdomain setup through newer updates.
Once you’ve well-versed yourself in the do’s and don’ts in email subdomains, there’s nothing to stop you. It’s up to your brand style and work strategy to successfully implement subdomains in your company’s communication.
Read also: 6 Email Sequence Templates For Better Conversions
Examples of Effective Email Subdomain Strategies
Using multiple subdomains for different email communication purposes can transform business communication. This approach makes communication more streamlined, segregated, secure, and easy to track and analyze.
Here are some examples of businesses that use email subdomains effectively.
Mailgun: Streamlined marketing communications
- Subdomain: learn.mailgun.com
- Strategy: Mailgun has a subdomain known as learn.mailgun.com to broadcast new messages, welcome messages to new users, or sign up for a new account.
- Outcome: This dedicated subdomain creates a clear division between marketing emails and transactional communications. So, when Mailgun has to work out its approach to acquiring first-time customers, it can be specific.
Braze: Personalized email addresses
- Subdomain: hello.braze.com
- Strategy: Braze uses the subdomain ‘hello.braze.com’ with senders’ names to make it look more personalized, such as [email protected].
- Outcome: This approach made it easy to enhance the brand image through personalization. This way of reaching out made Braze’s e-mail communications more unique and engaging to the person on the receiving end.
Google: Service-specific subdomains
- Subdomains: docs.google.com, slides.google.com
- Strategy: To fuel its ease-of-finding process, Google employs different subdomains for services such as Google Docs and Google Slides.
- Outcome: By separating services into separate subdomains, services are grouped, made easier for users to navigate and find, and distinguished from one another.
SoundCloud: Functional organization
- Subdomains: notifications.soundcloud.com, announcements.soundcloud.com
- Strategy: To improve the organization of received messages, SoundCloud uses subdomains to separate emails from notices and announcements.
- Outcome: This organizational approach then enhanced SoundCloud’s organization of emails and the overall user experience. The emails received are sorted out depending on the recipient’s organizational use.
Wallapop: Segmenting communication channels
- Subdomains: marketing.wallapop.com, dealers.wallapop.com
- Strategy: To distinguish marketing communication from the actual buy-sell communication currently handled via internal messages, Wallapop uses custom subdomains.
- Outcome: This segmentation is important to avoid confusing the two since the marketing messages to be sent differ from the professional ones. This, in turn, will ensure that Wallapop can send the appropriate messages to each segment.
Blumiblum: Dedicated subdomains for newsletters
- Subdomains: newsletter.blumiblum.com, news.blumiblum.com
- Strategy: For its newsletters, Blumiblum has separate subsections run under subdomains like newsletter.blumiblum.com and news.blumiblum.com.
- Outcome: It also helps Blumiblum evenly separate the newsletter’s operations and records and track chosen subscribers well enough to give them relevant content.
These case studies clearly show the possible ways of employing email subdomains and their positive impact on email-based practices.
The clever use of subdomains can help companies achieve better conversation rates and enhance their business outcomes in terms of segregation, customization, or classification of emails.
Read also: Avoiding the Spam Folder — An Intro to Email Deliverability
Conclusion
Email subdomains offer firms a powerful edge in managing their email systems. The benefits are clear: improved deliverability, better organization, and enhanced segmentation and personalization.
This post highlights how top organizations across various industries creatively use email subdomains to elevate their email marketing strategies. It’s time to consider how email subdomains can benefit your business, optimizing your email communication for maximum effectiveness.
Consider the potential—embrace email subdomains to transform your email marketing and achieve unprecedented success.
EngageBay is an all-in-one marketing, sales, and customer support software for small businesses, startups, and solopreneurs. You get email marketing, marketing automation, landing page and email templates, segmentation and personalization, sales pipelines, live chat, and more.
Sign up for free with EngageBay or book a demo with our experts.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQ)
1. What is the difference between an email subdomain and an email alias?
An email subdomain is a part of the main email domain assigned for a specific purpose, such as marketing. However, an email alias is another email address directly linked to your main email.
2. How do email subdomains impact email deliverability?
Subdomains in emails can enhance the deliverability rate since they separate the email traffic, increase the sender’s reputation, and foster trust in the email services.
3. Can I set up multiple email subdomains under one main domain?
Administrators also have the option to create several email subdomains for one main domain to differentiate the types of emails and their functions.
4. What are the security implications of using email subdomains?
Email subdomains help improve security by segregating email traffic; however, configuration of DNS and authentication is critical.
5. How do you troubleshoot common issues with email subdomains?
Request your service provider to verify the DNS records, double-check email client settings with your provider, and check email logs for troubleshooting.
