Inventory management is a critical task in every business. As companies try to keep track of their supplies, they face two significant challenges – overstocking and understocking.
When the latter happens, companies are pressured to retain their customers by replenishing out-of-stock items – this is a tactical approach.
But if there’s no defined strategy to achieve this, they may end up purchasing excess supplies that stay for extended periods on the shelves. An expensive move like this could incur unexpected losses, affecting business growth.
This article shares the five major causes of overstocking and some proven strategies to prevent overstocking. And, even if you already have overstocking problems, the tips shared in this guide will help you avoid unnecessary damages and product expirations.
Table of Contents
What Is Overstocking?
Overstocking means purchasing goods or supplies that exceed the company’s needs or market demands within a given period. It happens when a company over-orders inventory and ends up with excess stock.
When companies order too many products that they can’t sell, their inventory storage costs increase. And the products may likely go out of fashion or depreciate as they reach their expiration dates.
Will Stevenson, in his book, explained the challenges that come with overstocking. According to him,
“… overstocking unnecessarily takes up space and ties up funds that might be more productive elsewhere … the price tag for excessive overstocking can be staggering when inventory holding costs are high …”
What Are the Causes of Overstocking?
The first step to preventing excess stock is knowing the root of the problem. Although overstocking arises from several factors, you can compile them under these five major causes.

1. Poor inventory management
The sorting, storage, packaging, and overall inventory management enable businesses to track the entrance and exit of supplies. As the demands for different stock-keeping units (SKUs) change, either due to seasonality or changes in trends, it becomes more demanding to balance between having too much or too little.
Due to inaccurate reporting, poor communication between departments, or improper planning, companies may lack real-time insights into their inventory costs. These irregularities can cause retailers to over-order goods above maximum stock levels, leading to excessive warehousing and purchasing costs.
2. Supply chain management problems
Incidents like natural disasters, wars, or pandemics can disrupt a company’s supply chain, thus increasing the chances of stockouts or delayed production. When companies sense a potential barrier in the supply chain, they may want to avoid unexpected delays and disruptions by purchasing excess stock.
While this may be a perfect strategy to combat stockouts, it may lead to overstocking and a higher risk of damages or product expiration. For strategies on overcoming logistical challenges, understanding the nuances of efficient supply chain management can be crucial.
3. Inaccurate demand forecasting
You can make smart decisions about your inventory and product offerings using accurate qualitative and quantitative data, regardless of the location, seasonality, or product type.
But when you overestimate the demand or misinterpret customers’ behavior, you may end up stocking your shelves with excess supplies. And when the market demand for a particular SKU eventually slows down, the surplus goods will lie in the store for extended periods, taking up space that could be used for other products.
Read also: eCommerce Metrics Made Easy: How to Drive Growth
4. Fear of stockouts
Due to inefficient supply chain management, low production costs, or product quality issues, a company may unexpectedly run out of stock. According to Netstock, 43% of consumers indicated they are more likely to ditch a product after experiencing two or more stockouts.
As a result, many companies would rather overstock their shelves to avoid running out of supplies in the event of a natural disaster or any other challenge.
5. Seasonal demands
As seasons change, demands also change. Periods like Christmas, Easter, etc., come with an increase in customer demands, so store owners leverage these events to boost sales. But, as businesses tend to rack up inventory in preparation for the season, improper planning may push them to over-order stock.
When the seasonal buying windows close, the excess supplies lie untouched on the shelves for prolonged periods. This may be due to poor marketing, promotion, or pricing strategy.
Read also: Sales Forecasting: Comprehensive Guide For Small Business Owners
Overstocking Problems
From goods depreciation to limited storage spaces and tied-up cash, overstocking can result in several critical issues in businesses, regardless of the cause. Here are some problems that come with overstocking:
1. Increased storage and handling costs
One of the most obvious pitfalls of overstocking is the rise in inventory costs. Inventory costs refer to all expenses that involve inventory management, including storage, ordering, transportation, etc.
When you order too many supplies, you may end up storing them in spaces meant for other products. Since there’s a low demand for overstocked goods, sales and turnovers will be low. Moreover, the limited spaces for more stock may lead to higher chances of stockouts for other SKUs in high demand.
The longer the goods stay on the shelves, the higher the expenses and costs of preserving them until they are sold.
2. Product expiration and obsolescence
Typically, all products are time-sensitive. While some may last for a few weeks or months, others could stay up to a few decades.
When you purchase any product, you expect to sell it before it loses its value. However, in the event of overstocking, you have more stock than you can sell. And with changes in trends, a product may slowly become outdated.
The worth of an outdated product is usually reduced, especially when the demand gradually dies down. This is the same for perishable goods – they deteriorate when they stay longer than expected.
These damages may lead to unexpected losses, wasted resources, and additional expenses for repairs and replacements. Even more, you may be pressured to sell these products below the actual prices to free up more space.

3. Captive capital
When you rack up your inventory with new products, you have to sell them within a defined timeline to regain your capital and take your profits. But with overstocking, your funds are tied up in excess inventory.
With low capital, you cannot purchase new products in higher demand. This raises your stockout rate for other SKUs, eventually resulting in lost sales.
The losses may snowball as more needs arise to introduce new products or run other profitable business operations. Ultimately, there’s a higher risk of losing opportunities for expansion and scaling.
4. Reduced customer satisfaction
All other consequences of overstocking will eventually lead to a poor customer experience.
While trying to avoid stockouts by purchasing too many supplies, you may take excess space for new products and eventually, run out of stock for other fast-selling SKUs. When customers come to the store and discover the goods are unavailable, it leaves them with a poor experience.
Even more, customers, who purchase overstocked goods, will get frustrated when they see their items in poor condition. These experiences reduce brand trust, forcing customers to seek solutions from competitors.
Read also: Sales Analysis: Learn To Zoom In & Master the Pipeline
SKU Rationalization for Overstocking
There’s no fixed number for the right amount of stock a company should have, as different businesses have varying operations and sales processes. Moreover, the minimum and maximum stock levels for distinct SKUs within a company vary since the demands depend on several factors.
However, proper inventory management and accurate reporting can give retailers insights into products that sell well and others that sell slowly. As companies monitor their turnover rate, they can set minimum and maximum inventory levels for different SKUs.
Ultimately, proper SKU rationalization can help retailers identify and discontinue low-performing products.
Read also: What is Sales Planning? Tips & Downloadable Templates for Beginners
Overstocking vs Stockpiling
As companies prepare for challenging seasons or try to combat supply chain management issues, they may store large quantities of goods for future use, thus increasing product availability when demands escalate. This is stockpiling, not overstocking.
Though similar, overstocking and stockpiling are used when companies order too many supplies. However, they possess a few differences:
| Overstocking | Stockpiling | |
| 1. | Overstocking involves purchasing excess goods beyond customer demand | Stockpiling involves purchasing large quantities of goods for future demand |
| 2. | Overstocking results from poor inventory management and inaccurate forecasting | Proper inventory management and accurate demand forecasting help companies stockpile products to mitigate supply chain risks |
| 3. | There is a lack of communication between departments | There is proper communication between departments |
| 4. | Overstocking leads to wastage and losses | Stockpiling increases the availability of products and reduces shortages in the case of a disaster or an emergency. |
| 5. | Overstocking is an unplanned event | Stockpiling is a deliberate strategy to enhance product availability |
Read also: Ecommerce Marketing: 8 Areas to Focus on to Increase Sales
How to Avoid Overstocking Problems
Knowing the cause of overstocking is the first step toward proper inventory management. But it doesn’t end there. There are other strategies tailored towards helping you implement better stock practices. Here are preventive measures that reduce the risk of having too many supplies on your shelves:
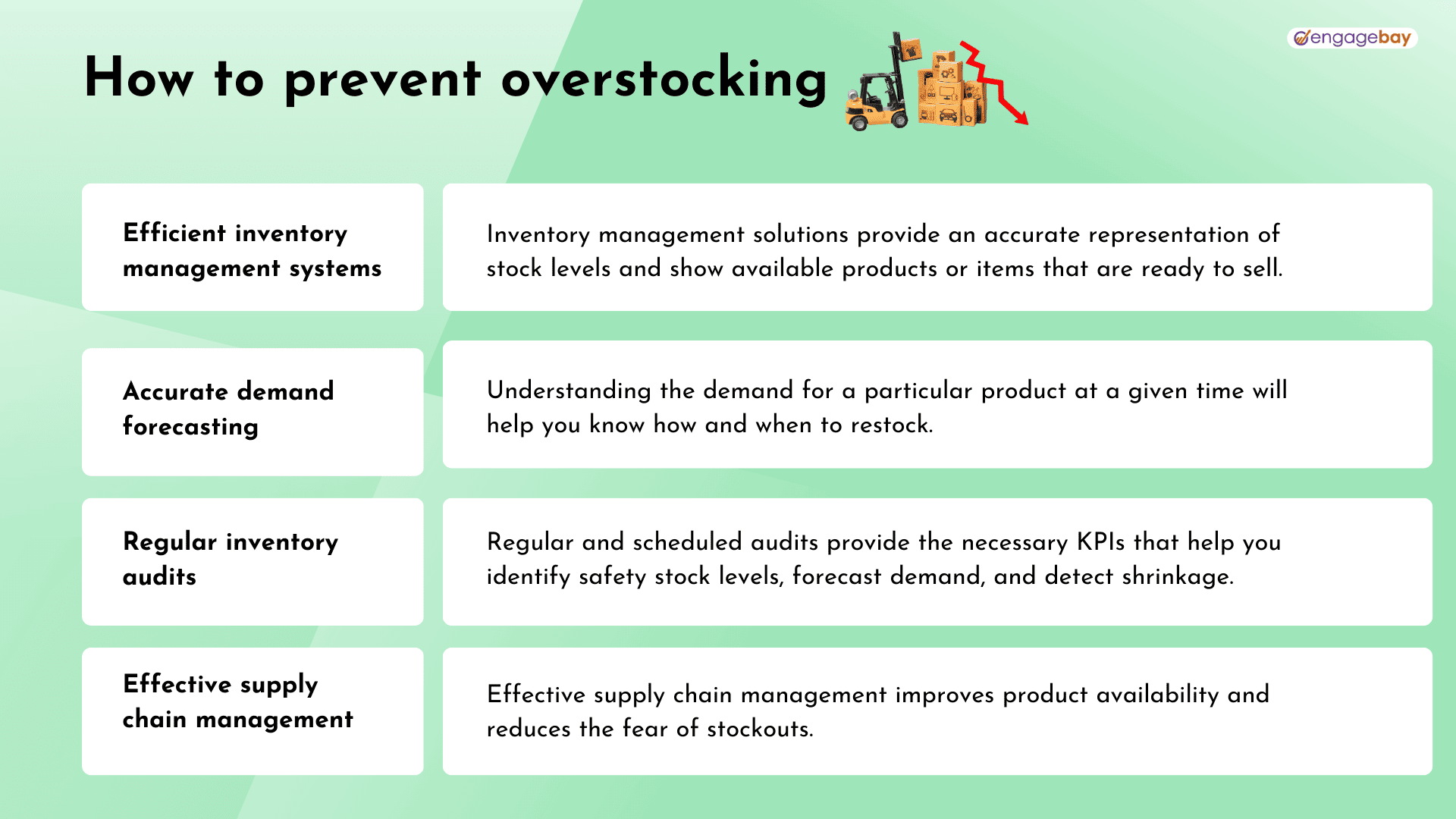
1. Efficient inventory management systems
An inventory management tool possesses capabilities for tracking inventory levels, product sales, orders, deliveries, and other production processes. Inventory management solutions provide an accurate representation of stock levels and show available products or items that are ready to sell.
With this data, you determine your optimal stock levels even as demands and trends change. By giving you insights into real-time data, the software programs help you make strategic purchasing decisions.
2. Accurate demand forecasting
By accessing marketing and industry trends, you can accurately forecast the demand for a particular SKU. This can help you identify factors that affect customer behavior within a specific period.
Using tools like Google Trends, Netstock, or SAP, you can accurately identify products that pique customers’ interests over time. With the data, you can set optimum inventory levels for several items, regardless of the seasons or changes in trends.
3. Regular inventory audits
Inventory audits involve using specific key performance indicators (KPIs) to match your current stock levels and inventory records with your financial data. Regular and scheduled audits help you identify safety stock levels, forecast demand, and detect shrinkage.
These KPIs include inventory turnover ratio, inventory count, average inventory, order fulfillment time, cycle time, inventory-to-sales ratio, etc.
A successful inventory audit gives you a complete view of your inventory, helping you identify bestselling and failing products. This gives insights into products you should restock more frequently and others you should ignore to avoid overstocking.
4. Effective supply chain management
Some numerous limitations and disruptions come with supply chain management. For fear of stockouts, these disruptions can pressure retailers to over-order excess supplies. But with efficient supply chain management, companies can craft clear strategies that ensure continuous inventory flow even with unexpected challenges.
Having supply chain resilience involves making plans and strategies to enhance product availability and ensure optimal stock levels.
Some of these strategies include having multiple distribution channels for inventory, collaborating with several suppliers and carriers that use TMS for fleet management, and employing experienced logistics specialists.
Also, retailers with multiple sales centers can rearrange stock levels based on the demand in a particular location. This creates a balance to ensure that an item is not overstocked in one location and understocked in another.
Read also: eCommerce Sales Funnels 101: A Beginner’s Guide
What To Do With Overstock Inventory
As much as overstocking can be prevented, many companies already have excess supplies on their shelves with no idea of what to do with them. Since the demand for these items is low and doesn’t sell well, there are other ways to take them off the shelves and free up your inventory space without incurring exponential losses.

1. Create special offers and discounts
You can pique your customers’ interests by reducing the prices of overstock inventory since the demand for the items is low. With other special offers like multi-buy, BOGO (buy one, get one free), etc., you attract potential buyers to buy more, especially if the items are part of a set.
Since the excess stock may stay longer than usual and depreciate, offering discounts will help you sell them faster while preventing unnecessary damages.
2. Move excess stock to other locations
This only applies to retailers who have multiple sale centers. Monitoring stock levels across several locations and transferring surplus inventory will ensure that an item is not overstocked in one location and understocked in another.
However, if there’s only one store, retailers can consider rearranging the products or optimizing their storefront to attract more buyers. This will make hidden products visible and easily accessible.
3. Offer surplus items as gifts or charitable donations
In line with creating special offers and discounts, merchants can also give surplus items as gifts. While this may not directly increase your profit, it can improve customer satisfaction.
This strategy works well for low-cost items, and retailers can use it to boost the sales of another product or improve their marketing campaigns.
Even more, some supplies can serve as donations to local organizations. This shows your support to the community, hence, boosting brand trust.
4. Request a refund or exchange
If you have a great relationship with your supplier, you can kindly request a refund or an exchange for a different item. This can only work if the goods are in good condition since the supplier will have to resell them to other customers.
Some suppliers have refund policies, so you can ask to be sure your supplier accepts this before presenting your offer.
5. Employ inventory liquidation services
Inventory liquidation involves selling off excess inventory in bulk at a reduced price. This occurs when businesses plan to shut down or take off excess stock.
Inventory liquidation firms purchase excess stock at heavily discounted prices. And while there could be a decrease in your profit margin, you get to free up space for other products that will perform better.
Be sure to compare options and check reviews to find reliable liquidators with workable policies.
Read also: Multichannel Retailing: Everything You Need to Know
Bottomline: Get a Grip on Your Inventory
One of the major causes of overstocking is poor inventory management. Ordering products without understanding your store’s inventory can lead to overstocking for some products and understocking for others.
However, a good inventory management system, alongside a fully functioning strategy will help you overcome fluctuations in stock levels.
Manually processing your inventory data may lead to inaccuracies, miscalculations, and other errors. So, you need an inventory management tool and a customer relationship management (CRM) system like EngageBay, to help you track sales, record customer data, and communicate with your buyers to improve sales efficiency and customer satisfaction.