Before prospects become customers, they undergo a process known as sales qualification.
One such sales qualifying framework is CHAMP – an acronym for CHallenges, Authority, Money, and Prioritization.
In this article, we will walk you through the definition of Sales CHAMP and how it can help your business.
Table of Contents
What Is the Sales CHAMP Framework?
Usually, the process of sales qualification includes cold calling or reaching out to prospects through emails and social media platforms.
But it’s not enough to simply inform prospects about your company’s products.
You need to understand them and their challenges first.
This will help you discover your target audience and build long-lasting relationships with them.
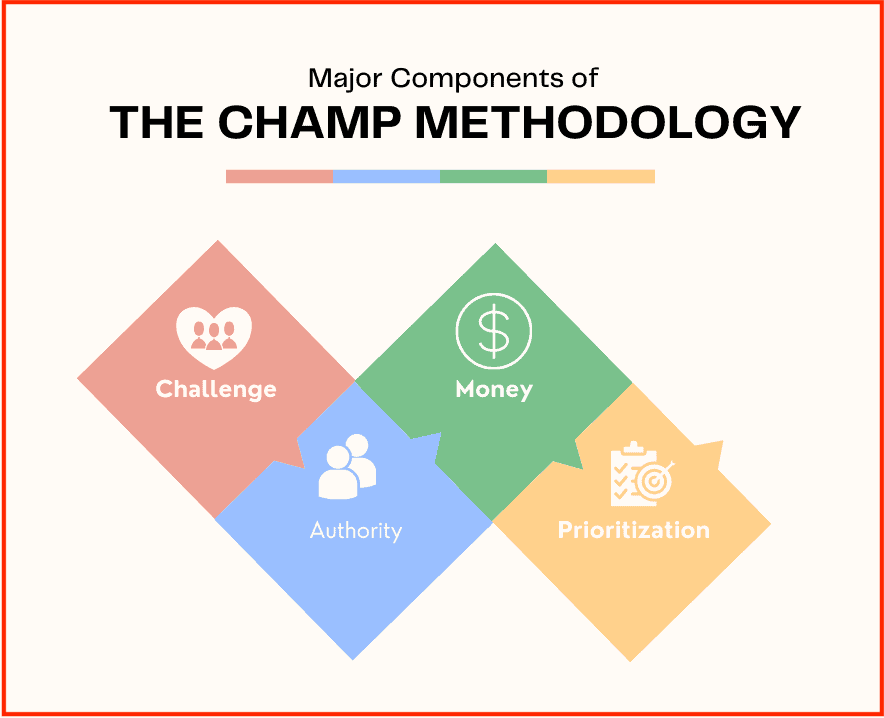
The sales CHAMP method starts off by finding out the challenges faced by potential customers and then selling them products that would resolve their problems.
Knowing which leads are more likely to become your customers save time, as sales teams become aware of which prospects to target.
Let’s dig deeper into the sales CHAMP methodology.
#1. CHallenges

The ‘CH’ in ‘CHAMP’ stands for ‘CHallenges.’
The first thing a sales rep needs to do is find out the challenge a prospect is facing.
This process helps in finding their ideal customers.
In fact, before CHAMP, BANT was one of the most popular approaches. It stands for Budget, Authority, Need, and Timeline.
While all the stages are equally important, sales professionals wondered if it was right to proceed with a budget rather than care about a lead’s challenge.
That’s how the CHAMP framework came in.
In the CHAMP framework, discovering challenges takes precedence over budget.
It allows sales teams to better qualify their prospects and address their pain points.
Once prospects understand how your brand can help overcome their challenges, it becomes easier to convince them to make a purchase.
On the other hand, if you had simply proposed a budget, you would have already disqualified the prospect.
This is because you would have only stated the cost of your products rather than how your brand can be beneficial or helpful for resolving the issues faced by potential customers.
So, how do you find out what challenges your prospects face? Here are some questions that you can ask.
- What are the challenges your company is facing?
- Tell me about the most pressing problems you need to resolve.
- How long have you been experiencing this problem?
- What led you to seek solutions now?
- What will happen if this problem is not resolved?
- What would your company’s operations look like if this problem were solved today?
Using the answers, you can convince prospects about your company’s products or services that would help address their challenges.
Read also: Cross-Selling Guide For Beginners (With Examples & Strategy)
#2. Authority

For sales and marketing teams, time is everything.
This is why you need to reach out to the right people to ensure that your time and efforts are headed in the right direction.
Before talking to a prospect, find out whether the individual is in a position of authority. Here, authority implies the decision-making powers of a person.
Such people need not necessarily be in a managerial or executive position; they could be working in the lower or middle management as well.
But what only matters is that the people you are talking to have the authority over buying decisions.
And if not, they should be able to direct you to people who can undertake decisions.
Below are examples of questions that you can ask to find out the authority of a person.
- Would you be the best person to speak with regarding this?
- What is your role in the decision-making process?
- Who, other than yourself, is involved in the decision-making process in the company?
- How are buying decisions made for a product like ours? Who is involved in looking at this solution?
- What are the concerns decision-makers may have? If there are any potential concerns, how do you think we should address them?
By asking such questions, you would be in a better position to find out authority figures in a company, helping you save time and directing your marketing efforts on the right path.
Read also: 12 Powerful Sales Growth Strategies (+ Calculations)
#3. Money

While money might not be the most important part of the sales CHAMP framework, one cannot ignore the role of money in sales.
Once you have figured out the challenges your prospects face, it is time to discuss their expectations regarding investment.
If prospects are unable to afford your brand, it would be difficult for you to make a sale.
You need to convince potential customers that the return on investment (ROI) will be far greater than the costs involved in buying your products.
To find out whether prospective buyers are willing to invest in your brand, ask the following questions:
- Have you set aside a budget for this product?
- Do you have a budget allocated for our product(s)?
- Who are the stakeholders involved in the budgeting process?
- When will your budget be available?
- What does the typical budget allocation process look like?
- What are your investment expectations necessary to purchase our product(s)?
Having answers to these questions will help you determine whether the prospect can afford to invest in your product or not.
Read also: Sales Quota 101: What It Is and Why It Matters to Your Business
#4. Prioritization

The final step in the sales CHAMP process is prioritization.
After you have determined that the client can and is willing to invest in your brand, you need to create a timeline.
The timeline includes the time frame required to resolve the company’s challenges, depending on its priorities.
However, you need to be very specific while preparing the timeline.
If a company is keen on addressing the issues immediately, it implies that your project is a top priority. Hence, your timeline will be shorter, and you need to deliver solutions faster.
Make sure the timeline is realistic and should be discussed before you start working on your products.
To determine the time frame required to address the company’s challenges, below is a list of questions that can help you get started.
- When do you want to solve this problem?
- When were you planning to implement the solutions?
- Do you have the time required to implement this project?
- How important is the project to you, and where does this stack up regarding priority and urgency?
- Are you looking for alternative solutions to this problem?
- What is the latest time period you would like to make a decision?
Once you have figured out the timeline, it is easy to find out how to implement the solution required to resolve the company’s issues.

Read also: Examples of Unethical Sales Practices and How to Avoid Them
Should You Always Use the Sales CHAMP Framework?
Even though the sales CHAMP framework is a great option for many sales teams, it might not be effective in every case scenario.
For instance, when it comes to selling to enterprise companies, the decision-making power doesn’t come down to just one individual.
Any large purchases may require sign-off from multiple people in an organization.
That’s why instead of just pointing to one single sale qualification framework, you might want to also try out a different approach.

Types of Sales Qualification Frameworks
There exist various sales qualification frameworks, including BANT, MEDDIC, FAINT, ANUM, and CHAMP.
Let us get a brief understanding of each one of them.
#1. BANT

BANT stands for ‘Budget, Authority, Need, and Timeline.’
Developed by IBM, it was one of the most commonly used sales qualification frameworks until recently.
It’s safe to say that the sales CHAMP framework is an improvised version of BANT. The BANT framework works as follows:
- Budget: It determines whether a prospect is capable of purchasing or investing in a company’s product or service. You can ask questions such as ‘Is the prospect capable of buying?’ or ‘Do you have a budget allocated for this purchase?’ to qualify leads.
- Authority: Authority refers to the decision-making powers of a prospect. If the prospect makes the final decision on placing an order, you can go ahead with the deal. If not, you need to find someone else to sell your products. That’s why you need to find out who has the authority to make purchase decisions.
- Need: ‘What challenges does the product solve?’ or ‘Why do you want to resolve this challenge?’ can make it easier for sales teams to understand the problems faced by potential clients and whether their products or services are useful for overcoming these issues.
- Timeline: The timeline determines when the prospect is planning to make a purchase. To find out the time period required by a potential client to buy your products, you can ask possible questions like ‘When do you need a solution?’ or ‘Do you have the time required to implement the solution?’
Read also: Return on Sales: Does Your ROS Make Sense Yet?
#2. MEDDIC
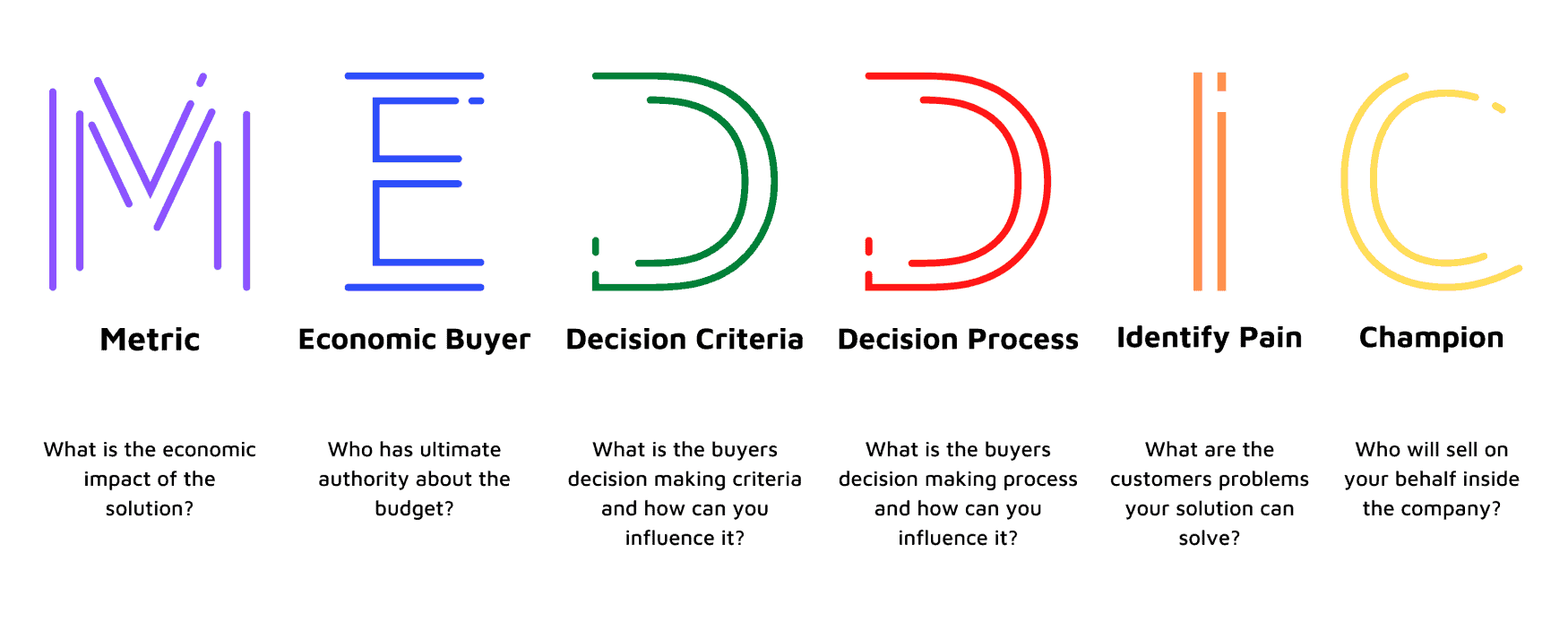
MEDDIC stands for Metrics, Economic Buyer, Decision Criteria, Decision Process, Identify Pain, and Champion.
It is ideal for companies that aim to transform buying patterns among customers.
Here is what the MEDDIC framework looks like.
- Metrics: Metrics determine how much money your product or service will earn depending upon its economic impact on your client’s company.
- Economic Buyer: The economic buyer is one who has the authority over the buying decisions of a company.
- Decision Criteria: It defines the factors that will impact the buying decisions of the lead for your company’s products or services.
- Decision Process: The decision process outlines the method by which the prospect decides whether to buy your product or service.
- Identify Pain: Pain identification refers to discovering the challenges faced by the lead, and how your company’s products can help address these issues.
- Champion: Once you have identified your prospect’s pain points, the last step includes finding out the people or experts who would be selling your products.
Read also: 8 SMART Sales Goals for Business Growth [+ Case Study]
#3. FAINT
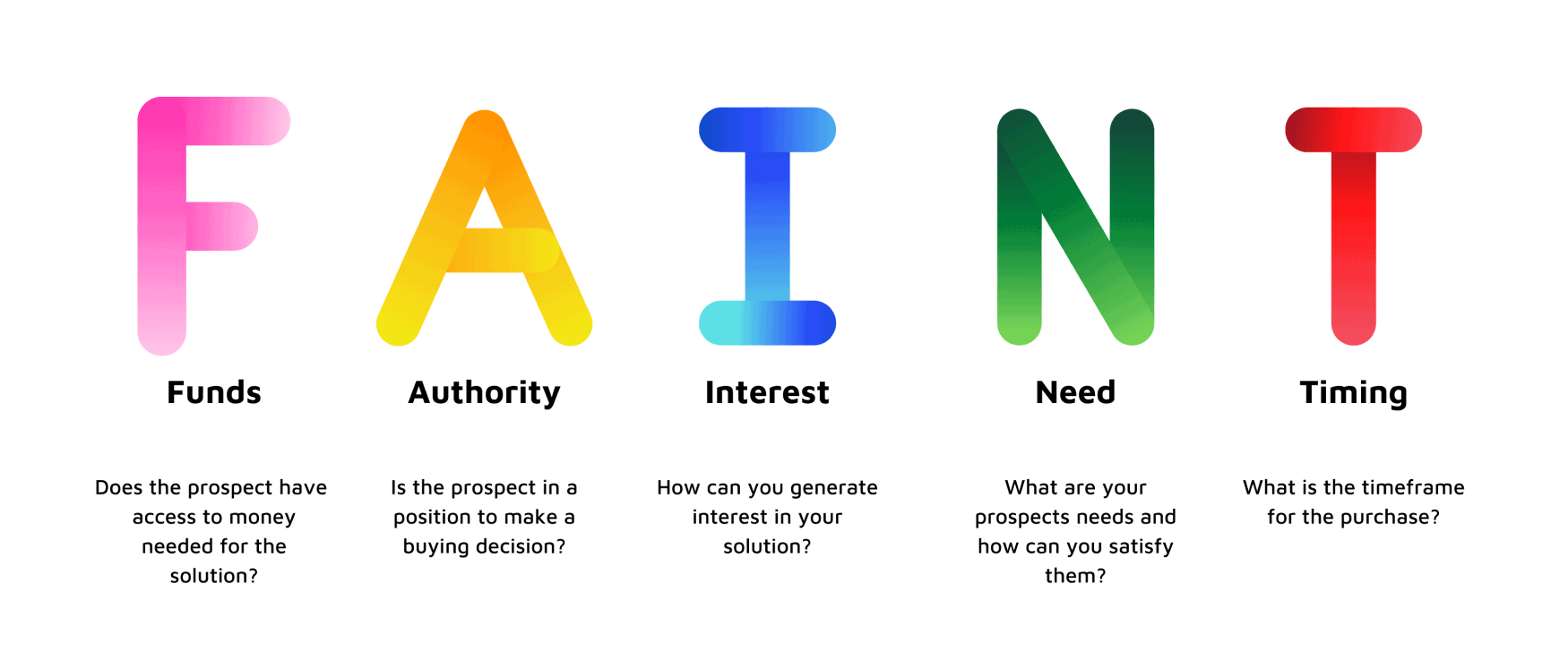
FAINT stands for Funds, Authority, Interest, Need, and Timing.
It is typically used by companies that aim at acquiring high-end brands or wealthy individuals as their target audience.
Below is a description of how FAINT works:
- Funds: As the name suggests, ‘Funds’ indicates targeting people with big bank accounts or those that are willing to shell money for your products and services.
- Authority: It helps you find and target leads with decision-making powers over purchases.
- Interest: Once you have determined the leads that are willing to pay for your product, it is time to gauge their interest. In this step, companies inform prospects about their firm and its products, with the aim of persuading them to place an order.
- Need: The ‘Need’ aspect helps you discover the problems faced by your prospective customers, and how your brand can deliver solutions.
- Timing: The last step in the FAINT process is ‘Timing’ and refers to the timeline required to implement your project.
Read also: The Challenger Sales Model: A 5-Min Guide to Close More Deals
#4. ANUM

ANUM refers to Authority, Need, Urgency, and Money.
Unlike other frameworks that begin by discovering the challenges and budgetary constraints of prospects, the ANUM framework focuses primarily on the decision-making powers of its leads.
Let us look at how ANUM works.
- Authority: The first step in the ANUM process is ‘Authority’ and indicates whether the lead has any decision-making powers. If yes, then sales reps can proceed with the deal. If not, companies should target people who have decision-making authority.
- Need: This step helps firms find out the challenges and needs of prospective clients and how their products can meet those needs.
- Urgency: It determines how soon the lead wants solutions or needs to be met.
- Money: Once brands have figured out how they can help their prospects, it is time to find out whether the latter can pay for their products or not. This is the final step in the ANUM framework.
Read also: What Is a Sales SPIFF? The Game-Changing Motivator for Sales Teams
Wrap Up
The CHAMP methodology is considered among the best in the lead qualification process.
By implementing the sales CHAMP framework, it becomes easier for you to discover the challenges faced by potential buyers and how your company can help address them.
It also helps determine whether a buyer is worth your time, depending on their decision-making authority, willingness to invest, and available timeline.
As a result, you can better narrow down your target market and create solutions that cater to their needs.
A sales automation and CRM software can complement and aid in your frameworks — EngageBay is among the highest-rated.
Try EngageBay for free now 🙂